NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 6 | Thermodynamics |
| 6.1 | Thermodynamic Terms |
| 6.2 | Applications |
| 6.3 | Measurement of ∆U and ∆H: Calorimetry |
| 6.4 | Enthalpy Change, ∆rH of a Reaction – Reaction Enthalpy |
| 6.5 | Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions |
| 6.6 | Spontaneity |
| 6.7 | Gibbs Energy Change and Equilibrium |
NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Textbook QUESTIONS SOLVED
Question 1. Choose the correct answer:
A thermodynamic state junction is a quantity
(i) used to determine heat changes
(ii) whose value is independent of path
(iii) used to determine pressure volume work
(iv) whose value depends on temperature only.
Answer: (ii) whose value is independent of path
Question 2. For the process to occur under adiabatic conditions, the correct condition is:
(i) ∆T= 0 (ii) ∆p = 0
(iii) q = 0 (iv) w = 0
Ans. (iii) q = 0
Question 3. The enthalpies of all elements in their standard states are : ‘
(i) unity (ii) zero
(iii) < 0 (iv) different for each element
Answer: (ii) zero
Question 4.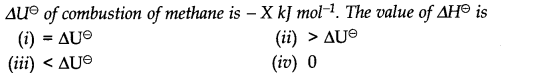
Answer:
Question 5. The enthalpy of combustion of methane, graphite and dihydrogen at 298 K are -890.3 KJ mol-1, – 393.5 KJ mol-1 and – 285.8 KJ mol-1 respectively. Enthalpy of formation of CHJg) will be
(i) – 74.8 KJ mol-1 (ii) – 52.27 KJ mol-1
(iii) + 74.8 KJ mol-1 (iv) + 52.26 KJ mol-1
Answer: As per the available data :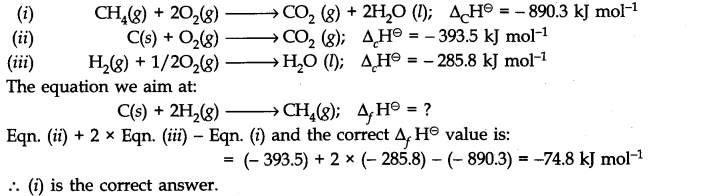
Question 6. A reaction, A + B—>C + D + q is found to have a positive entropy change. The reaction will be
(i) possible at high temperature (ii) possible only at low temperature
(iii) not possible at any temperature (iv) possible at any temperature
Answer: (iv) possible at any temperature
Question 7. In a process, 701 ] of heat is absorbed by a system and 394 J of work is done by the system. What is the change in internal energy for the process?
Answer: Heat absorbed by the system, q = 701 J Work done by the system = – 394 J Change in internal energy (∆U) = q + w = 701 – 394 = 307 J.
Question 8. The reaction of cyanamide,NH2CN(s) with dioxygen was carried out in a bomb calorimeter and ∆U was found to be -742,7 KJ-1 mol-1 at 298 K. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction at 298 K.NH2CN (S) + 3/202(g) —–>N2(g) + CO2(g) + H20(Z)
Answer: ∆U = – 742.7 KJ-1 mol-1 ; ∆ng = 2 – 3/2 = + 1/2 mol.
R = 8.314 x 10-3KJ-1 mol-1 ; T = 298 K
According to the relation,∆H = ∆U+∆ngRT
∆H = (- 742.7 kj) + (1/2 mol) x (8.314 x10-3 KJ-1 mol-1 ) x (298 K)
= – 742.7 kj + 1.239 kj = – 741.5 kj.
Question 9. Calculate the number of kj of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 60 g of aluminium from 35°C to 55°C. Molar heat capacity of Al is 24 J mol-1 K-1.
Answer: No. of moles of Al (m) = (60g)/(27 g mol-1) = 2.22 mol
Molar heat capacity (C) = 24 J mol-1 K-1.
Rise in temperature (∆T) = 55 – 35 = 20°C = 20 K
Heat evolved (q) = C x m x T = (24 J mol-1 K-1) x (2.22 mol) x (20 K)
= 1065.6 J = 1.067 kj
Question 10. Calculate the enthalpy change on freezing of 1.0 mol of water at 10.0°C to ice at – 10.0°C. A, H = 6.03 KJ mot1 at 0°C. Cp [H20(l)J = 75.3 J mol-1 K-1; Cp [H20(s)J = 36.8 J mol-1 K-1.
Answer: The change may be represented as: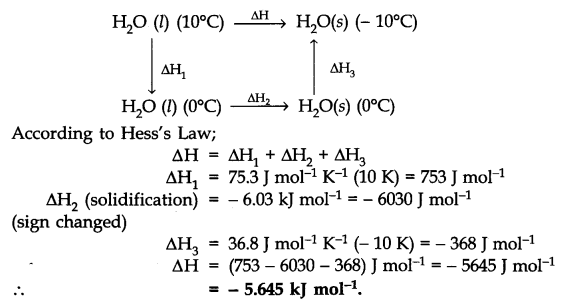
Question 11. Enthalpy of combustion of carbon to carbon dioxide is – 393.5 J mol-1 .Calculate the heat released upon formation of 35.2 g of C02 from carbon and oxygen gas.
Answer: The combustion equation is:
C(s) + 02 (g) —–> C02(g); AcH = – 393.5 KJ mol-1
Heat released in the formation of 44g of C02 = 393.5 kj
Heat released in the formation of 35.2 g of C02=(393.5 KJ) x (35.2g)/(44g) = 314.8 kj
Question 12. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction:
N204(g) + 3CO(g) ———->N20(g) + 3CO2(g)
Given that;∆fH–CO(g) = – 110 kj mot-1; ∆fHC02(g) = – 393 kj mol-1
∆fHN20(g) = 81 kj mot-1; ∆fN2O4(g) = 9.7 kj mol-1
Answer: Enthalpy of reaction (∆r,H) = [81 + 3 (- 393)] – [9.7 + 3 (- 110)]
= [81 – 1179] – [9.7 – 330] = – 778 kj mol-1
Question 13. Given : N2(g) + 3H2(g) ————> 2NH3(g); ∆r H– = -92.4 kj mot-1 What is the standard enthalpy of formation of NH3 gas?
Answer: ∆H– NH3 (g) = – (92.4)/2 = – 46.2 kj mol-1
Question 14. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CH3OH. from the following data:
(i) CH3OH(l) + 3/2 02 (g) ———-> CO2 (g) + 2H20 (l); ∆rH– = – 726kj mol-1
(ii) C(s) + 02(g) —————>C02 (g); ∆cH– = -393 kj mol-1
(iii) H2(g) + 1/202(g) —————->H20 (l); ∆fH– = -286 kj mol-1
Answer: The equation we aim at;
C(s) + 2H2(g) + l/202(g) ———> CH3OH (l);∆fH– = ±? … (iv)
Multiply eqn. (iii) by 2 and add to eqn. (ii)
C(s) + 2H2(g) + 202(g) ————->C02(g) + 2H20(Z)
∆H = – (393 + 522) = – 965 kj moH Subtract eqn. (iv) from eqn. (i)
CH3OH(Z) + 3/202(g) ————> C02(y) + 2H20(Z); ∆H = – 726 kj mol-1
Subtract: C(s) + 2H2(y) + l/202(g) ———-> CH3OH(Z); ∆fHe = – 239 kj mol-1
Question 15.
Answer: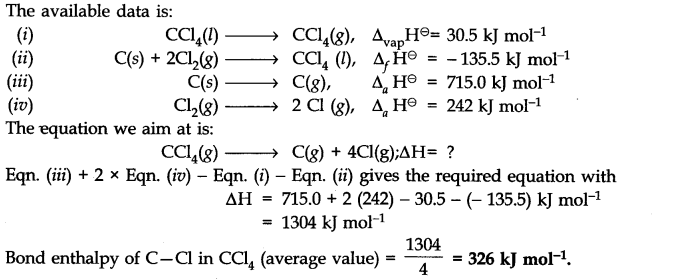
Question 16. For an isolated system∆U = 0; what will be ∆S?
Answer: Change in internal energy (∆U) for an isolated system is zero for it does not exchange any energy with the surroundings. But entropy tends to increase in case of spontaneous reaction. Therefore, ∆S > 0 or positive.
Question 17. For a reaction at 298 K
2A + B————->C
∆H = 40Q kj mot1 and AS = 0.2 kj Kr-1 mol-1.
At what temperature will the reaction become spontaneous considering ∆H and ∆S to be constant over the temperature range?
Answer: As per the Gibbs Helmholtz equation:
ΔG = Δ H- TΔ S For ΔG=0 ; ΔH=TΔS or T=ΔH/ΔS
T = (400 KJ mol-1)/(0.2 KJ K-1 mol-1) = 2000 k
Thus, reaction will be in a state of equilibrium at 2000 K and will be spontaneous above this temperature.
Question 18. For the reaction; 2Cl(g) ———-> Cl2(g); what will be the signs of ∆H and ∆S?
Answer: ∆H : negative (- ve) because energy is released in bond formation
∆S : negative (- ve) because entropy decreases when atoms combine to form molecules.
Question 19.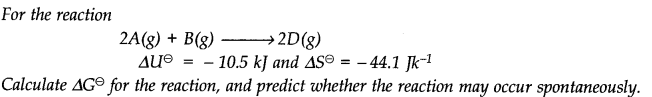
Answer:
Question 20.![]()
Answer: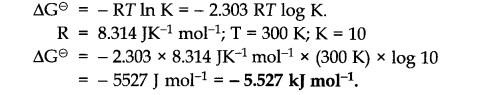
Question 21.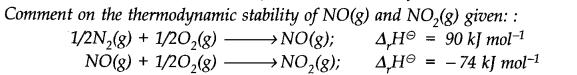
Answer: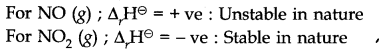
Question 22.![]()
Answer: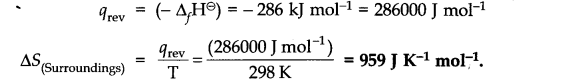
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. If ∆U = 0 how are q and w related to each other?
Answer: ∆U = q + w
Question 2. When is bond energy equal to bond dissociation energy ?
Answer: For diatomic molecules e.g. H2, O2, Cl2 etc. both energies are equal.
Question 3. What is the enthalpy of formation of the most stable form of an element in its standard state?
Answer: It is zero.
Question 4. Out of diamond and graphite, which has greater entropy?
Answer: Graphite has greater entropy since it is loosely packed.
Question 5. At what temperature entropy of a substance is zero?
Answer: At absolute zero.
Question 6. From thermodynamic point of view, to which system the animals and plants belong?
Answer: Open system.
Question 7. Predict the sign of ∆S for the following reaction heat
CaCO3 (s) ———> CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Answer: ∆S is positive.
Question 8. State Hess’s law.
Answer: The change of enthalpy of a reaction remains same whether the reaction is carried out in one step or several steps.
∆H = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3……………
Question 9. What is the enthalpy change for an adiabatic process?
Answer: For an adiabatic process,∆H = 0
Question 10. What do you mean by entropy?
Answer: Entropy is a measure of randomness of a system.
Question 11. Give a relation between entropy change and heat absorbed or evolved for a reversible reaction occurring at temperature T.
Answer: ∆s = qrev/T
Question 12. What is the condition for spontaneity in terms of free energy change?
Answer: If ∆G is negative, process is spontaneous.
If ∆G is positive, the process is non-spontaneous.
If ∆G = 0, the process is in equilibrium.
Question 13. What is an adiabatic process?
Answer: The process in which no exchange of heat takes place between the system and the surroundings.
Question 14. What is free energy in terms of thermodynamics?
Answer: Free energy of a system is the capacity to do work.
G = H-T∆S
Question 15. Define extensive properties.
Answer: Properties which depend upon the amount of the substance are called as extensive properties.
Question 16. How are internal energy change, free energy change and entropy change are related to one another?
Answer: ∆G = ∆H – T∆S (At constant pressure)
Question 17. How is entropy of a substance related to temperature?
Answer: On increasing temperature, entropy of a substance increases.
Question 18. Define intensive properties.
Answer: Properties which depend on the nature of the substance and not on the amount of the substance are called intensive properties.
Question 19. What is Gibbs Helmholtz equation?
Answer: ∆G = ∆H – T∆S
Where ∆G = free energy change.
∆H = enthalpy change.
∆S = entropy change.
Question 20. What are the units of entropy?
Answer: SI unit of ∆S =JK-1mol-1 .
Question 21. What is a spontaneous change? Give one example.
Answer: A process which can take place of its own or initiate under some condition.
For example: Common salt dissolves in water of its own.
Post a Comment