NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 5 | States of Matter |
| 5.1 | Intermolecular Forces |
| 5.2 | Thermal Energy |
| 5.3 | Intermolecular Forces vs Thermal Interactions |
| 5.4 | The Gaseous State |
| 5.5 | The Gas Laws |
| 5.6 | Ideal Gas Equation |
| 5.7 | Kinetic Energy and Molecular Speeds |
| 5.8 | Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases |
| 5.9 | Behaviour of Real Gases: Deviation from Ideal Gas Behaviour |
| 5.10 | Liquefaction of Gases |
| 5.11 | Liquid State |
NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
Question 1. What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 at 30°C?
Answer: P1 = 1 bar,P2 = ? V1= 500 dm3 ,V2=200 dm3
As temperature remains constant at 30°C,
P1V1=P2V2
1 bar x 500 dm3 = P2 x 200 dm3 or P2=500/200 bar=2.5 bar
Question 2. A vessel of 120 mL capacity contains a certain amount of gas at 35°C and 1.2 bar pressure. The gas is transferred to another vessel of volume 180 mL at 35°C. What would be its pressure?
Answer: V1= 120 mL, P1=1.2 bar,
V2 = 180 mL, P2 = ?
As temperature remains constant, P1V1 = P2V2
(1.2 bar) (120 mL) = P2 (180mL)
Question 3. Using the equation of state PV = nRT, show that at a given temperature, density of a gas is proportional to the gas pressure P.
Answer: According to ideal gas equation
PV = nRT or PV=nRT/V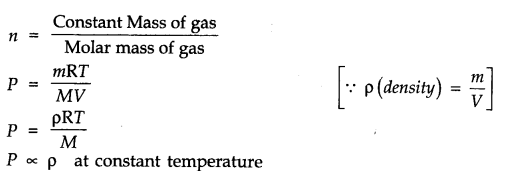
Question 4. At 0°C, the density of a gaseous oxide at 2 bar is same as that of dinitrogen at 5 bar. What is the molecular mass of the oxide?
Answer: Using the expression, d =MP/RT , at the same temperature and for same density,
M1P1 = M2P2 (as R is constant)
(Gaseous oxide) (N2)
or
M1 x 2 = 28 x 5(Molecular mass of N2 = 28 u)
or M1 = 70u
Question 5. Pressure of l g of an ideal gas A at 27°C is found to be 2 bar. When 2 g of another ideal gas B is introduced in the same flask at same temperature, the pressure becomes 3 bar. Find the relationship between their molecular masses.
Answer: Suppose molecular masses of A and B are MA and MB respectively. Then their number of moles will be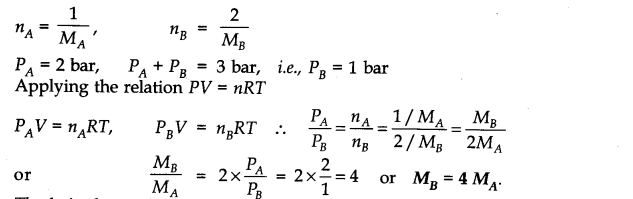
Question 6. The drain cleaner, Drainex contains small bits of aluminium which react with caustic soda to produce dihydrogen. What volume of dihydrogen at 20 °C and one bar will be released when 0.15g of aluminium reacts?
Answer: The chemical equation for the reaction is
2 Al + 2 NaOH + H20 -> 2 NaAl02 + 3H2 (3 x 22400 mL At N.T.P)
2 x 27 = 54 g.
54 g of Al at N.T.P release
H2 gas = 3 x 22400 0.15 g of Al at N.T.P release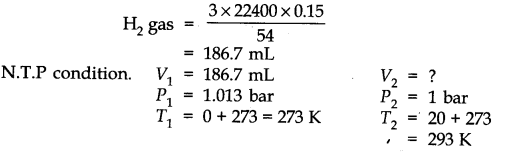
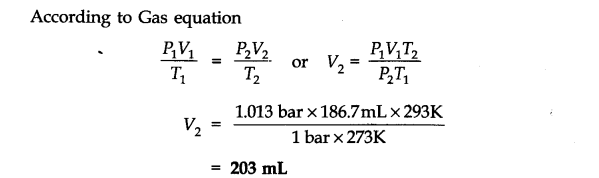
Question 7. What will be the pressure exerted by a mixture of 3.2g of methane and 4.4g of carbon dioxide contained in a 9 dm3 flask at 27 °C?
Answer: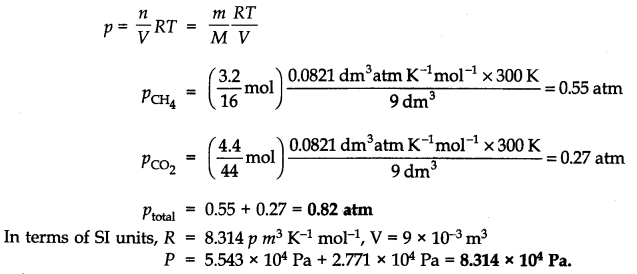
Question 8. What will be the pressure of the gas mixture when 0.5 L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0 L of dioxygen at 0.7 bar are introduced in all vessel at 27 °C?
Answer: Calculation of partial pressure of H2 in 1L vessel P1= 0.8 bar,
P2= ? V1= 0.5 L , V2 = 1.0 L
As temperature remains constant, P1V1 = P2V2
(0.8 bar) (0.5 L) = P2 (1.0 L) or P2 = 0.40 bar, i.e., PH2 = 0.40 bar
Calculation of partial pressure of 02 in 1 L vessel
P1‘ V1 = P2‘V2‘
(0.7 bar) (2.0 L) = P2 (1L) or P2‘ = 1.4 bar, i.e.,Po2= 1.4 bar
Total pressure =PHz + PQ2 = 0.4 bar + 1.4 bar = 1.8 bar
Question 9. Density of a gas is found to be 5.46 g/dm3 at 27 °C and at 2 bar pressure. What will be its density at STP?
Answer: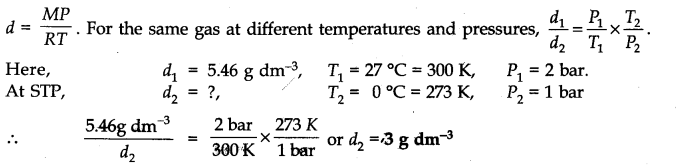
Question 10. 34.05 mL of phosphorus vapour weighs 0.0625 g at 546°C and 1.0 bar pressure. What is the molar mass of phosphorus?
Answer: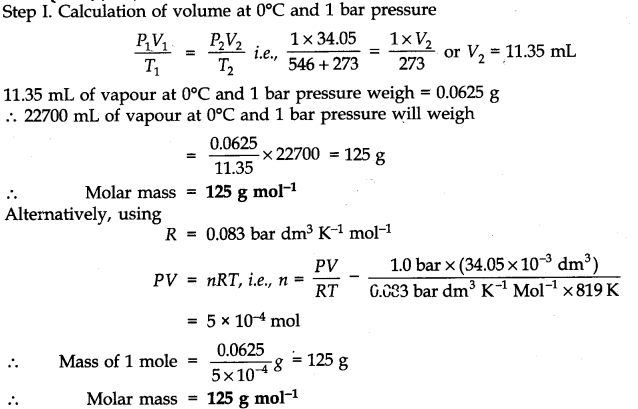
Question 11. A student forgot to add the reaction mixture to the round bottomed flask at 27 °C but instead, he/she placed the flask on the flame. After a lapse of time, he realized his mistake, and using a pyrometer, he found the temperature of the flask was 477 °C. What fraction of air would have been expelled out?
Answer: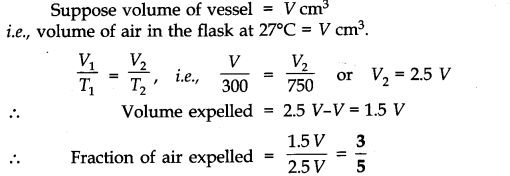
Question 12.Calculate the temperature of 4.0 moles of a gas occupying 5 dm3 at 3.32 bar (R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1)
Answer: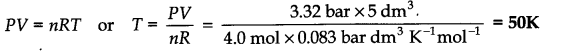
Question 13. Calculate the total number of electrons present in 1.4 g of dinitrogen gas.
Answer: Molecular mass of N2 = 28g
28 g of N2 has No. of molecules = 6.022 x 1023 1.4 g of
N2 has No. of molecules = 6.022 x 1023 x 1.4 g/28 g
= 3.011 x 1022 molecules.
Atomic No. of Nitrogen (N) = 7
1 molecule of N2 has electrons = 7 x 2 = 14
3.011 x 1022 molecules of N2 have electrons
= 14 x 3.011 x 1022
= 4.215 x 1023 electrons.
Question 14. How much time would it take to distribute one Avogadro number of wheat grains if 1010 grains are distributed each second ?
Answer: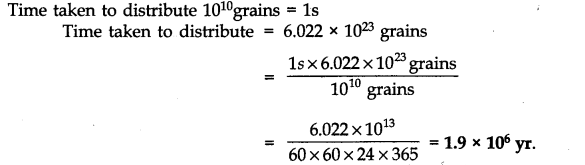
Question 15. Calculate the total pressure in a mixture of 8g of oxygen and 4g of hydrogen confined in a vessel of l dm3 at 27°C. R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1.
Answer: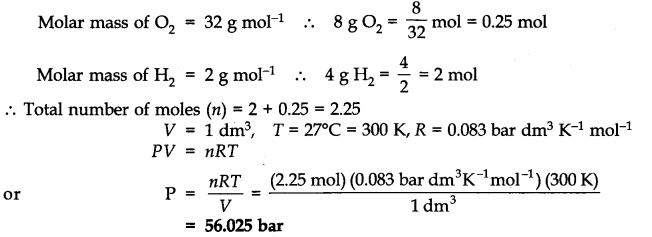
Question 16. Pay load is defined as the difference between the mass of the displaced air and the mass of the balloon. Calculate the pay load when a balloon of radius 10 m, mass 100 kg is filled with helium at 1.66 bar at 27°C (Density of air = 1.2 kg m-3 and R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1).
Answer:
Question 17. Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of CO2 at 31.1 °C and 1 bar pressure. R = 0.083 bar LK-1 mol-1
Answer: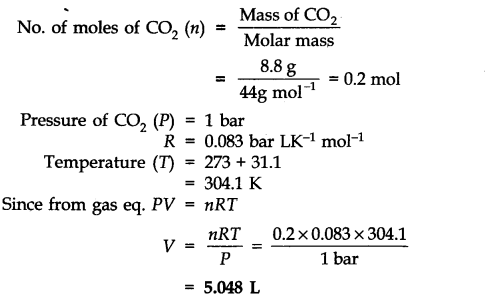
Question 18. 2.9 g of a gas at 95°C occupied the same volume as 0.184 g of hydrogen at 17°C at the same pressure. What is the molar mass of the gas ?
Answer: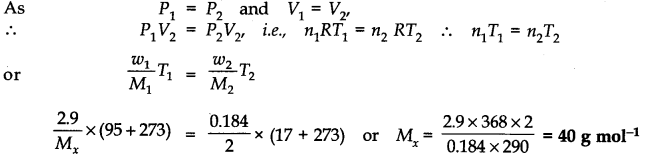
Question 19. A mixture of dihydrogen and dioxygen at one bar pressure contains 20% by weight of dihydrogen. Calculate the partial pressure of dihydrogen.
Answer: As the mixture H2 and O2 contains 20% by weight of dihydrogen, therefore, if H2 = 20g, then O2 = 80g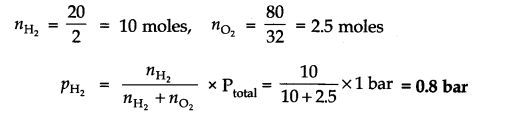
Question 20. What would be the SI unit for the quantity PV2T2/n?
Answer: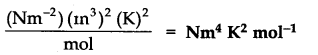
Question 21. In terms of Charles’ law explain why -273°C is the lowest possible temperature.
Answer: At -273°C, volume of the gas becomes equal to zero, i.e., the gas ceases to exist.
Question 22. Critical temperature for CO2 and CH4 are 31.1°C and -81.9°C respectively. Which of these has stronger intermolecular forces and why?
Answer: Higher the critical temperature, more easily the gas can be liquefied, i.e., greater are the intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, Co2 has stronger intermolecular forces than CH4.
Question 23. Explain the physical significance of vander Waals parameters.
Answer: ‘a’ is a pleasure of the magnitude of the intermolecular forces of attraction, while b is a measure of the effective size of the gas molecules.
Post a Comment